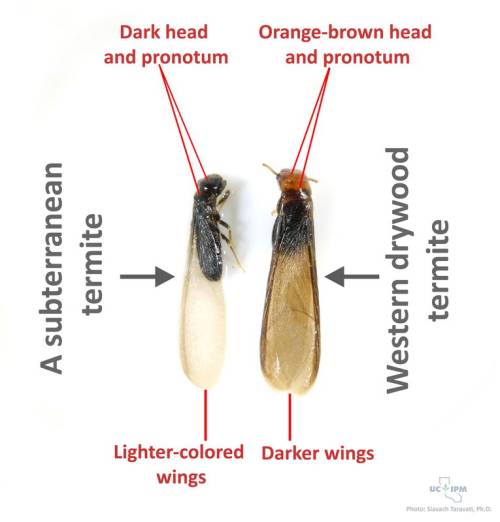
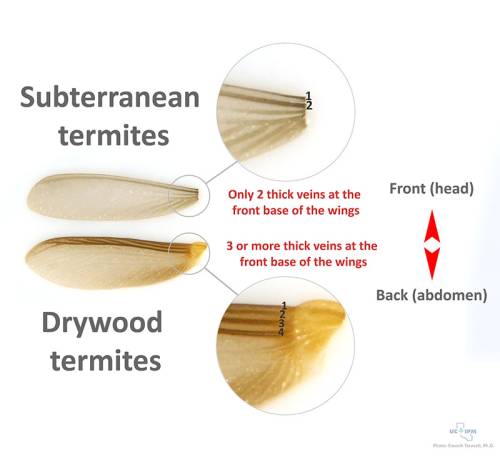
Termite Inspection Reports And How To Interpret Them
|
|
Published: 2024-2-04
|
You have just received your termite inspection report. Now what? What does it all mean? When you are buying a home, you are committed to paying at least several hundred thousand dollars plus interest throughout the loan. So why not make sure that the skeleton of your future house is sound?
Although rarely visible to us, most houses in the U.S. are mostly made of wood. Specifically, most of the structural skeleton of houses is made of wood. This includes roof trusses, sheathings, rafters, beams, posts, studs, floor and roof joists, window and door frames, porches and decks, fascia and subfascia, and baseboards. Also, most cabinets, gazebos, pergolas, and outdoor fences are made of wood.
All these wooden materials attract some uninvited guests such as termites, carpenter ants, and wood-boring beetles. Termites feed on wood as a food source, and depending on the species, as a nesting site, too. Wood is all that termites feed on (except some exotic termite species that grow fungi in their nest as food).
Purchasing a home can be very stressful. Working with a mortgage lender or bank, your realtor, making an offer, doing inspections, and negotiating the final offer price can be all overwhelming. A termite report is an important part of the home inspection which can tell you where the termites or termites damages are located. A termite inspection report should not be taken lightly, as it has very important information on the integrity of a house. A severely damaged house is not safe to live in and can potentially collapse as a result of earthquakes, storms, and other physical disturbances.
Problems with termite inspection reports
Termite reports are very useful pieces of information that tell us the status of termite damage in a building. However, interpreting termite reports is not as easy as it sounds. There are several problems associated with termite inspection reports:
They can be vague
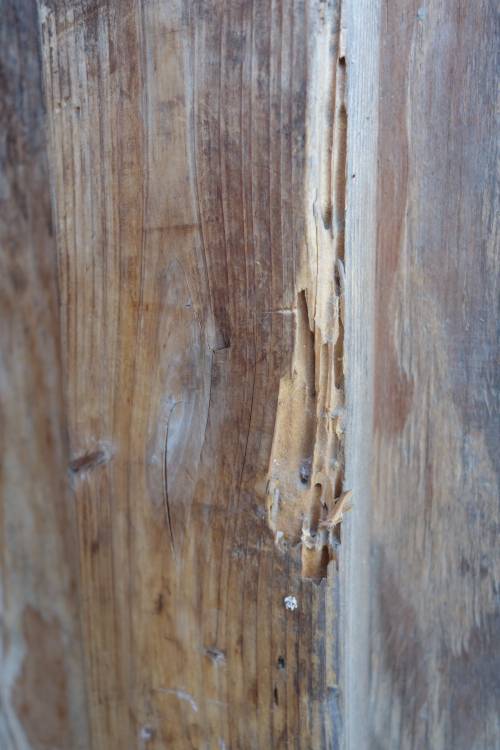
Termite inspection reports may mention the general areas in which termite infestation or damage is found but they rarely pinpoint the exact location and the extent of the infestation in a structure. Photos that accompany a termite inspection report help us to pinpoint the location of termite damage, but the severity of damage is not always visible in photos. Even when damage is visible, it is often hard to reliably rate the amount of damage without opening up walls and cutting and drilling structural wood.
Furthermore, recommended methods of termite treatment may lack reasoning on why such methods are recommended and the pros and cons of each. For example, in the case of drywood termites, it’s hard to know why a pest control company is recommending fumigation over local treatments and vice versa.
They often lack information on the biology of termites
Each termite species has a different colony structure and total number of termites per colony, nesting site preference, swarming (flight of winged termites) seasonality and preferred swarming time (day or night), moisture requirements, etc. These biological traits have significant implications when choosing the management method. For example, fumigating a house using sulfuryl fluoride (SF) gas for subterranean termites is useless, since their nest is always in the ground and SF has limited penetration into the soil. Similarly, treating a subterranean termite colony using liquid insecticides without fixing moisture and conducive conditions may only provide a temporary fix. Conducive conditions include settings that promote termites around the house such as storing a lot of firewood on the ground or having a lot of moisture buildup immediately around the house.
Consequently, it is very important for both the buyer and seller to understand the biology of the culprit termite.
They may miss important information
A termite inspector may easily miss a termite infestation or damages caused by them if they don’t thoroughly probe exterior surfaces. Also, it is not too uncommon for a pest control inspector to misidentify a termite species. This is because termites sometimes leave very little direct evidence behind to be used for identification purposes. This will cause false negative reports. A false negative result is produced when there is an actual infestation in a structure, but it is missed because the evidence is not visible to an inspector. Furthermore, patching and painting the exterior and interior of a house may hide termite damage evidence, leading to more false positive inspection results. In other cases, old termite damage and other evidence may convince an inspector to think that the building is still infested with live termites, a false positive result.
How we can help you with your termite report
We are here to help answer your questions about the termite infestations in your current or future home and to help you decide on the best course of action against these wood-destroying insects. We can answer the following questions during a phone or video call, or via email:
- Is the infestation in my house severe, based on my termite report?
- Do I really need to replace all the damaged wood to protect my home?
- What are the main types of termites and how their biology differs from each other?
- What are the most effective ways to treat termite infestations in my current or future home?
- How did termites get into my property in the first place?
- How often do I need to treat for termites?
- What if the previous owner never treated for termites?
- How to protect my house against future termite invasions?
- Drywood termites
- Fumigation
- What is structural fumigation and how it is done?
- Is it necessary to fumigate my current or future house? -Is fumigation safe and what are the potential risks? -Is fumigation the same as using bug bombs? -Is whole-structure fumigation effective? -For how long fumigation will protect my house?
- Heat treatment -What is heat treatment and how it is different from fumigation?
- Localized treatments
- What is a local termite treatment?
- Is it necessary to do local termite treatment?
- Are local treatments for termites effective?
- What chemicals and products are commonly used for local treatment of termites?
- For how long local treatment of termites will protect my house?
- Are there any health and environmental risks when treating termites locally?
- Subterranean termites
- Liquid insecticide treatment
- Common active ingredients and products
- Are liquid termite products effective?
- For how long liquid termiticides will protect my house?
- What are the application methods for liquid termiticides?
- Bait stations
- What is a termite bait station?
- What are the active ingredients in termite bait stations?
- Is termite baiting generally effective?
- How termite baiting will protect my house?
- Liquid insecticide treatment
- Formosan subterranean termite (FST)
- What are Formosan subterranean termites?
- Why FST is so destructive?
- What is the difference between aerial vs. subterranean colonies?
- Do FSTs damage live trees?
- What are the best options for treating FSTs?